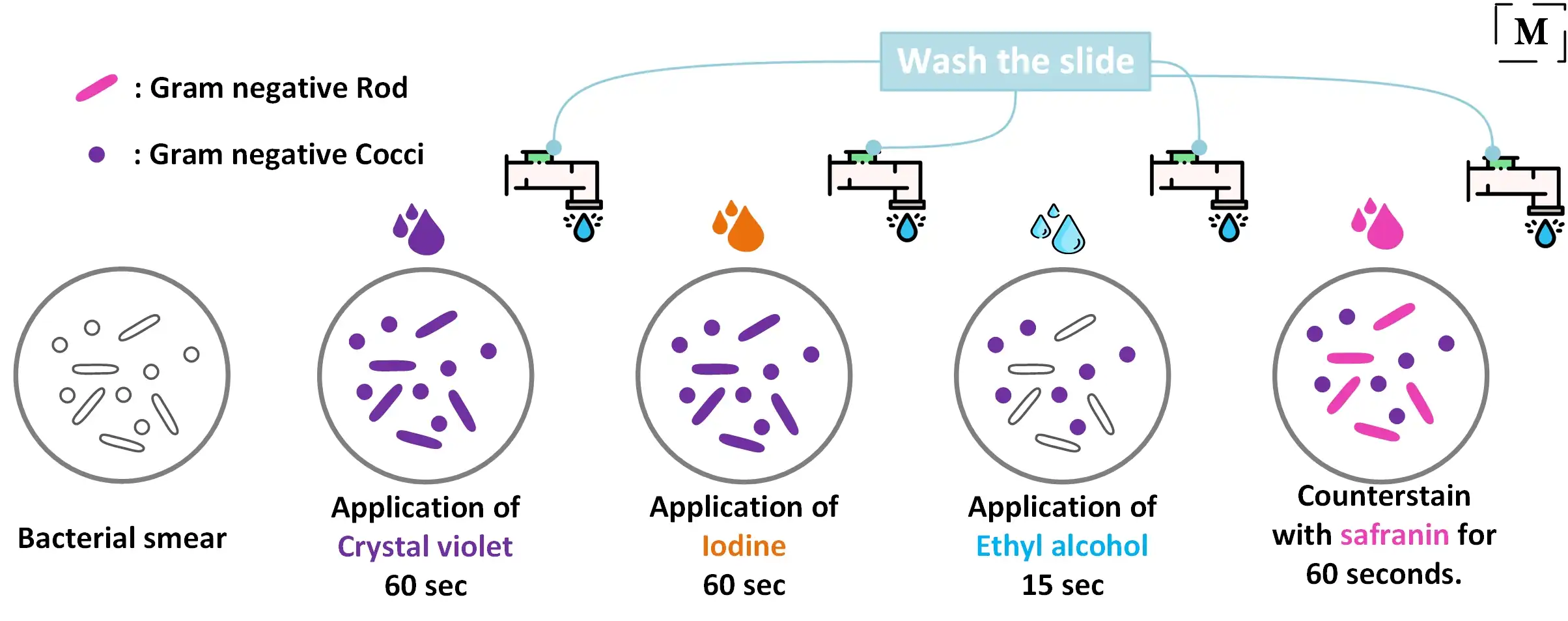
Next a Grams iodine solution iodine and potassium iodide is added to form a complex between the crystal violet and iodine. On the basis of their reaction to the Gram stain bacteria can be divided into two large groups.
Gram Staining Better Understanding Of The Procedure And Easy Interpretation Of The Results
Iodine increases the interaction between cell dye so that cell stains strongly.
. Carbolfuchsin stain 03 gm of basic fuchsin 10 ml of ethanol 95 volvol 5 ml of phenol heat-melted crystals 95 ml of distilled water. Gram staining is a differential staining technique which separates bacteria into two groups Gram-positive bacteria and Gram-negative bacteria. Mix and let stand for several days.
It aids in the diagnosis of a specific organism and tells the difference between gram negative and gram positive bacteria. We have evaluated the way in which the choice of fluorescent label can impact the detection of MHC multimer binding T cells in an ex. Congo red to color background Simple stain.
INTRODUCTIONHematoxylin and eosin HE stains have been used for at least a century and are still essential for recognizing various tissue types and the morphologic changes that form the basis of contemporary cancer diagnosis. Stain or dye is the synthetic chemical which is derived from nitrobenzene or aniline. Gram positive and Gram negative.
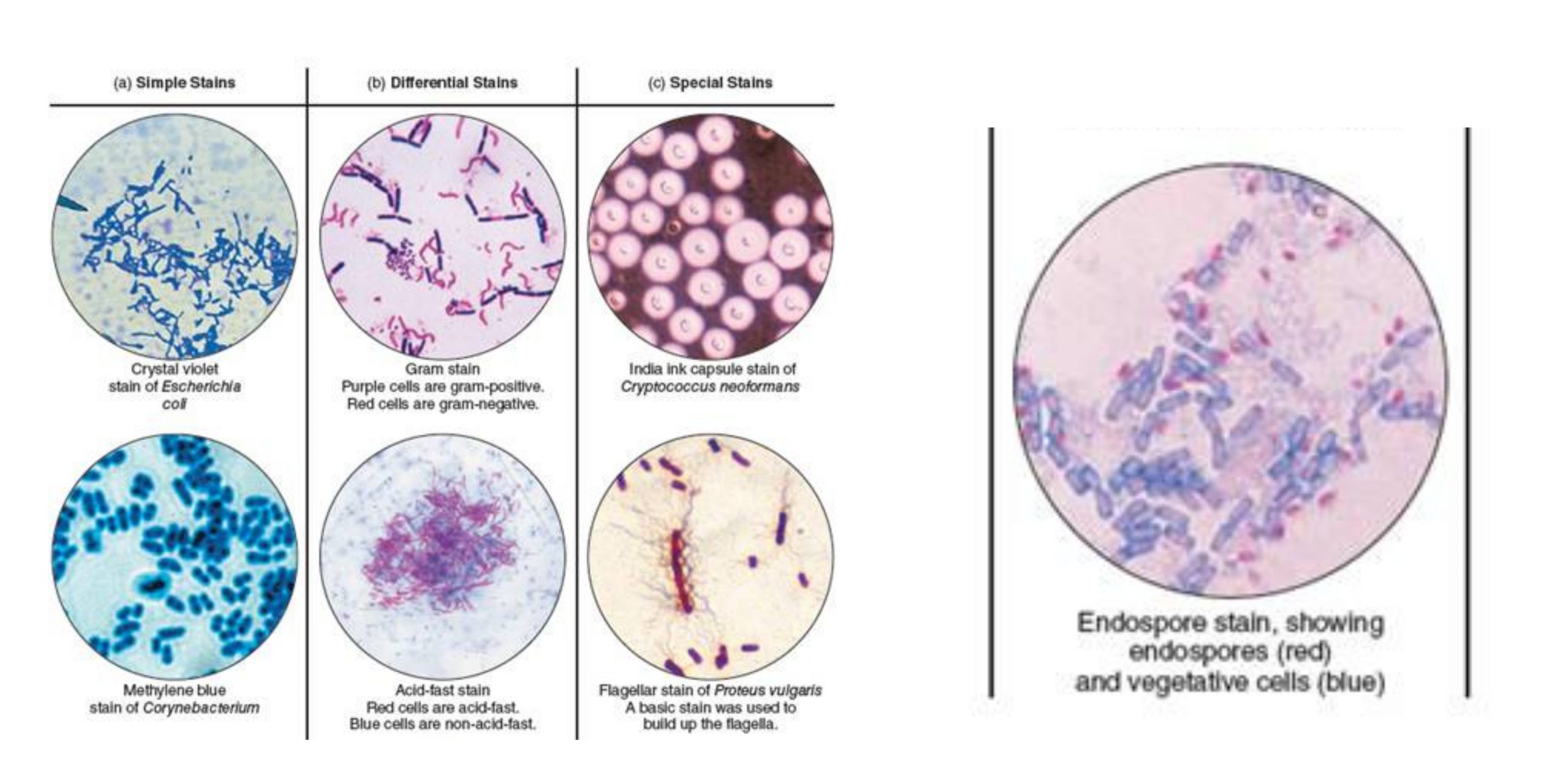
Acid Fast stain is a differential stain used to identify acid-fast organisms from non acid fast organisms. OBJECTIVES To be familiar with or be able to describe. The Gram stain is the differential stain that stains the bacterial cells differently according to the type of cell wall.
This complex is a larger molecule than the original crystal violet stain and iodine and is insoluble in water. Primary Stain Crystal violet is the commonly used primary stain in gram staining. The cells of Mycobacteria species appear red whereas non-acid fast bacteria appear blue.
The stain has been unchanged for many years because it works well with a variety of fixatives and displays a broad range of. Both gram-positive and gram-negative cells have. PROCEDURE OF NEGATIVE STAINING TECHNIQUE.
This stain imparts its colour to all cells. Procedure of Grams Staining. Then add the phenol dissolved in the water.
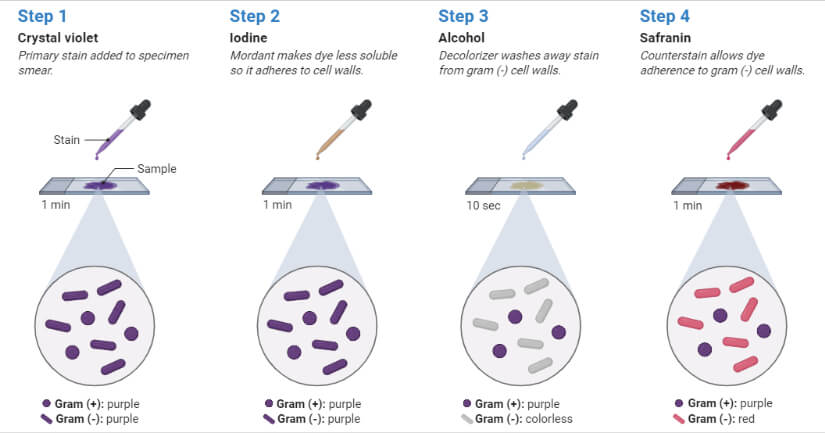
Dyes bind with cellular constituents producing color contrast and increasing their visibility. The smear is next decolourized by washing with ethanol or acetone. The process involves three steps.
Fast stain differentiates an important group of bacteria the mycobacteria on the basis of lipid content of their cell wall. A smear is subjected to heat after staining with Zeihl Neelson Carbol fuschin. Cells are stained with crystal violet dye.
This test differentiate the bacteria into Gram Positive and Gram Negative Bacteria which helps in the classification and differentiations of microorganisms. 1 Difference between simple and differential staining methods. Synonyms for on a regular basis include periodically regularly religiously rhythmically and with regularity.
Gram stain is used to differentiate the bacterial cells by staining the cell wall and distinguish two major groups of bacteria that are gram-positive and gram-negative. Take a clean Dry Scratch and Grease free Microscopic glass slide and place a drop of India ink or Nigrosin on it at one end near the edge. The latter are used mainly for the bacterial stain preparations.
The primary stain crystal violet binds to peptidoglycan coloring cells purple. A heat fixed smear is covered with a basic violet dye Example. Based on the types and number.
Capsular staining is a combination of two staining techniques. The steps of. Manevals stain to color the cell proper of the bacteria.
Do not take up stain and appear colorless between the dark background and the stained bacteria. The procedure is based on the reaction between peptidoglycan in the cell walls of some bacteria. Take a small portion of the bacterial colony with the help of sterilized Inoculating loop.
Endospore Staining by Dorners Method. The process of giving colour to particular organism or components of its is known as staining. The Gram stain procedure is a differential staining procedure that involves multiple steps.
The different response of the two groups to the Gram stain is based on fundamental differences in cell wall structure and composition. Gram Staining is the common important and most used differential staining techniques in microbiology which was introduced by Danish Bacteriologist Hans Christian Gram in 1884. The Gram stain involves staining bacteria fixing the color with a mordant decolorizing the cells and applying a counterstain.
Gram-positive bacteria appear violet in colour and gram-negative bacteria appear pink in colour as a. In the first step the smear is stained with basic dye crystal violet Primary stain followed by treatment with iodine solution functioning as mordant. 2 Theoretical and chemical basis of Gram stain procedure.
Simple staining is unable to highlight the exact organism. NEGATIVE STAINING SPREADER METHOD STEP 1. Classification Based on Purpose of Use.
In the Gram stain cells from a culture are spread in a thin film over a small area of a slide dried and then fixed by heating or with a chemical fixative to make the cells adhere to the glass slide. Acid-fast staining is based upon the principle of staining the bacterial cell relative to their cell wall differences. Important synthetic stains are safranin fast green amiline blue methylene blue crystal violet eosine acid fuchsin orange-G etc.
It is referred to as a primary stain since it is applied first. Hence we use dyes to stain cells. Dissolve the basic fuchsin in the ethanol.
Grams Staining comprises of four steps. During steam carbol fuschin penetrates the bacterial cell. Stains are used commonly in microbiology to increase the contrast between microorganisms or parts of its and the backgroundso that it can be easily visible.
The most important and widely used differential stain for bacteria is the Gram stain. Stains can be categorized as under on the basis of the purpose of their use. 3 Relationship between Gram staining and physiology of the microbe 4 Role of chemicals used during the Gram staining procedure 5 Appearance of Gram positive cells and.
Gram staining highlights different bacteria types through the use of special dyes. Simple stain - A staining procedure involving only one stain that can be used to determine cell shape size and arrangement differential stain - A staining procedure involving two stains that can be used to differentiate one component or cellular structure from another or to differentiate an entity from another in a specimen. Positively charged cationic dyes such as methylene blue crystal violet safranin etc bind with negatively charged cellular constitutents such as nucleic acids and acidic polysaccharides and cell surface of bacteria.
It was developed by Danish microbiologist Hans Christian Gram in 1884 as an effective method to distinguish between bacteria with different types of cell walls and even today it remains one of the most frequently used staining techniques. A large variety of fluorescent molecules are used on a regular basis to tag major histocompatibility complex MHC multimers for detection of antigen-specific T cells.

Gram Staining Principle Reagents Procedure Steps Results

Types Of Staining Techniques Used In Microbiology Microbe Online
0 Comments